|
Cr-doped ITO films as electrode in Spintronic Devices
We report on the growth and structural characterization
of very thin (20 nm) Cr-doped ITO films, deposited at room temperature by
double-target pulsed laser ablation on amorphous silica substrates. The role
of Cr atoms in the ITO matrix is carefully investigated with increasing
doping content by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Selected-area
electron diffraction, conventional bright field and dark field as well as
high-resolution TEM analyses, and energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy
demonstrate that (i) crystallization features occur despite the low growth
temperature and small thickness, (ii) no chromium or chromium oxide
secondary phases are detectable, regardless of the film doping levels, (iii)
the films crystallize as crystalline flakes forming large-angle grain
boundaries; (iv) the observed flakes consist of crystalline planes with
local bending of the crystal lattice. Thickness and compositional
information about the films are obtained by Rutherford back-scattering
spectrometry. Results are discussed by considering the combined effects of
growth temperature, smaller ionic radius of the Cr cation compared with the
trivalent In ion, doping level, film thickness, the double-target doping
technique and peculiarities of the pulsed laser deposition method.
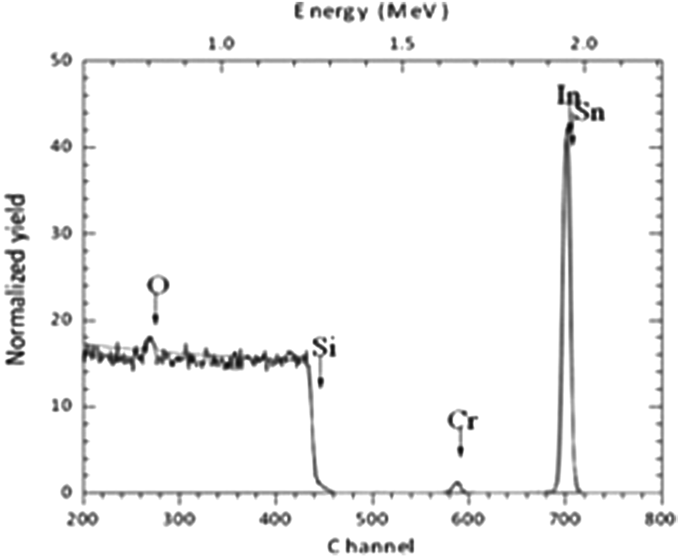
Figure 1.
RBS spectrum of the PLD sample.
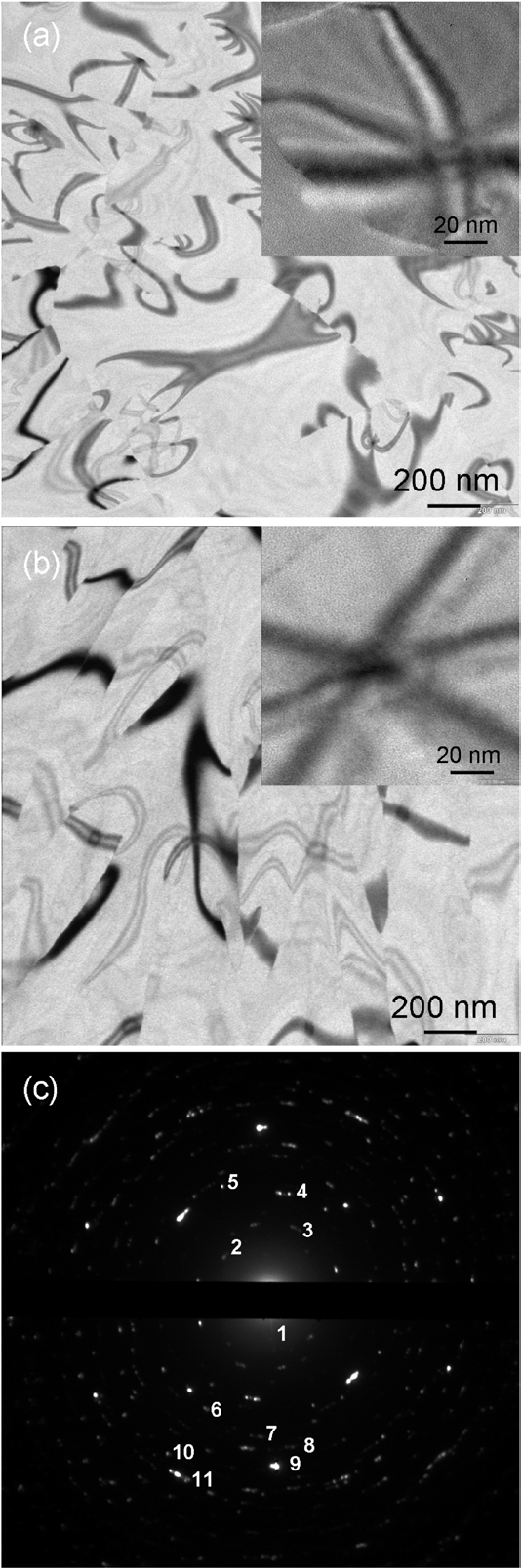
Figure 2. BF
TEM images of the LD (a)
and HD (b)
samples and their typical SAED pattern (c).
The numbering of the diffraction spots is related to the indexing of the
pattern.
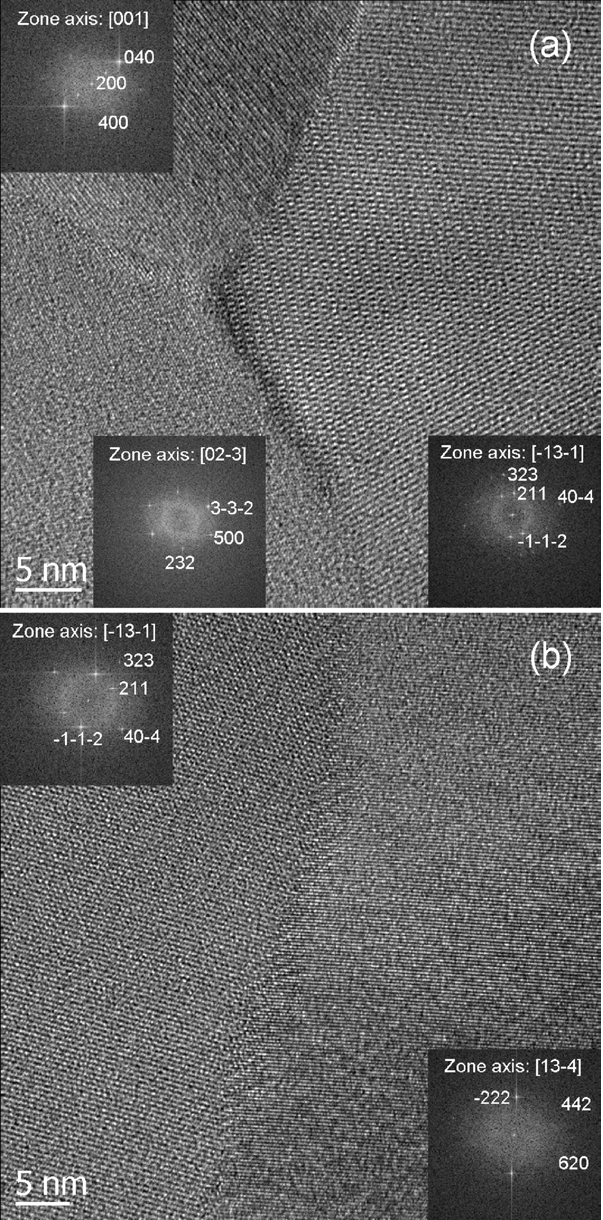
Figure 3.
HRTEM images of a typical GB region of the LD (a)
and HD (b)
films.
|
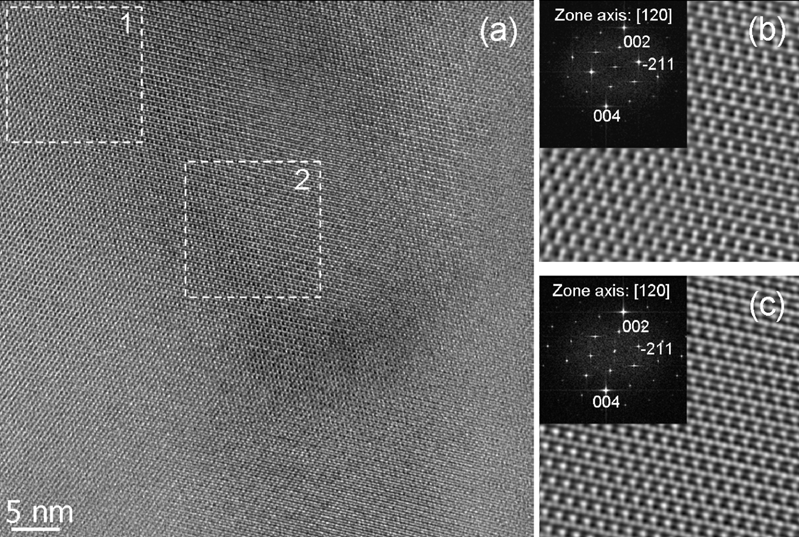
Figure 4. HRTEM image obtained from a
high-symmetry bending-contour figure of the HD sample (a). FFTs (inset) and
filtered inverse FFTs (b), (c) obtained from the regions in the dashed
rectangles 1 and 2, respectively. |
|
